
Both venous obstruction and the resulting inflammation can lead to valvular damage, reflux, and venous hypertension.
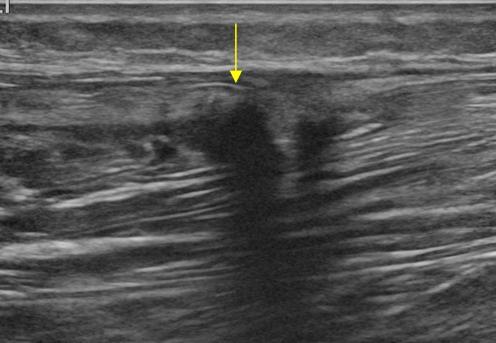
The cumulative incidence after symptomatic DVT is 15% to 50%, with most cases developing in 1 to 2 years. Postthrombotic syndrome (PTS) refers to the late complications of venous thromboembolism. Risk factors broadly extend from Virchow's triad of stasis of blood flow, endothelial injury, and hypercoagulability. In particular, iliofemoral DVT has a high incidence of recurrent hospitalizations and postthrombotic venous ulceration. The more proximal the blood clot, the more clinically crucial adequate management is. The annual incidence of DVT is 1 in 1000, and DVT is responsible for > 250,000 hospitalizations a year in the United States. Venous thromboembolism refers to the formation of blood clots in the venous structures. The US is also used to monitor disease progression over time. Furthermore, duplex ultrasound can delineate venous anatomy, valvular abnormalities and reflux, the extent and pattern of disease, and in doing so, help plan treatment. When evaluating acute deep venous thrombosis (DVT), ultrasonography is 97% sensitive for proximal DVT and 57% sensitive for calf DVT. It is noninvasive and offers no radiation risk to the patient. Venous duplex ultrasound is quick to perform and easily accessible. Peripheral venous ultrasound (US) is commonly used to diagnose and evaluate venous disease, including acute thromboembolism, postthrombotic syndrome, and chronic venous insufficiency. Outline how interprofessional team coordination can improve diagnostic results when using vascular sonography to evaluate conditions for which it is indicated.Describe the typical imaging findings of acute versus chronic deep venous thrombosis and valvular insufficiency.
ULTRASOUND OF LEG VEINS HOW TO
Explain how to perform a complete duplex ultrasound exam of the lower extremity peripheral venous system, including assessing for thrombosis as well as valvular insufficiency.Review the general pathophysiology of venous thrombosis, post-thrombotic syndrome, and chronic venous insufficiency.

This activity describes how to perform a complete duplex ultrasound exam of the peripheral venous system and highlights the interprofessional team's role in evaluating and managing care for patients with these conditions. Duplex ultrasound of the peripheral venous system is an easily accessible and reliable method of diagnosis, evaluating the extent and severity of the disease and monitoring progression and planning treatment. Acute DVT and chronic venous disease are common conditions with a significant burden on patient morbidity, mortality, and quality of life.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
